单元测试
很长一段时间以来,单元测试并不是前端工程师应具备的一项技能,但随着前端工程化的发展,项目日渐复杂化及代码追求高复用性等,促使单元测试愈发重要,决定整个项目质量的关键因素之一
概念
单元测试
单一的代码单元
- 类
- 对象
- 函数
- ...
FIRST原则
快速(Fast):单元测试执行一定要快,这样研发同学可以在项目周期的任意时间点,可以方便地执行单元测试,即便是有几千个单元测试也不影响。这些单元测试最好在几秒内运行完并返回期望的结果。(Isolated):每一个测试用例运行时、准备环境变量时或测试前环境搭建过程中,都是隔离的。过程中,不能有相互依赖,这样最终的测试结果可以不受其它因素的影响。(Repeatable) 执行:单元测试可以在不做任何修改情况下,在任何环境下执行。如果单元测试不依赖网络或数据库,单元测试失败原因的排查中,就不用考虑这方面的原因,毕竟单元测试依赖的只是被测试类或方法中的代码。这个原则,可以方便地让自己的单元测试逻辑保持良好的价值。试中自校验 (Self-validating):写了单元测试后,咱们不能再依赖肉眼观察,看被测代码的结果是否正确。测试代码自身会明白无误地告诉咱哪条测试用例失败了。(Timely):按 TDD 的理念,应该在相应的业务代码之前定单元测试。这一点上,大家可以自己掌握是否采用 TDD 的开发理念。不过,这个的理念是,即时地写单元代码,即便是很小的代码也是这样。
集成测试
一组需要运行多个测试进行验证的过程,通常是为了验证各个程序单元一起工作时的结果是否符合预期
验收测试/功能测试
从产品/用户角度对整个系统进行的测试,判断系统是否满足用户的验收条件。例如使用Selenium对Web应用进行自动化测试。
TDD
Test Driven Development:测试驱动开发
一种开发方式,以测试来驱动整个项目,即先根据接口完成测试编写,然后在完成功能时要不断通过测试,最终目的是通过所有测试。
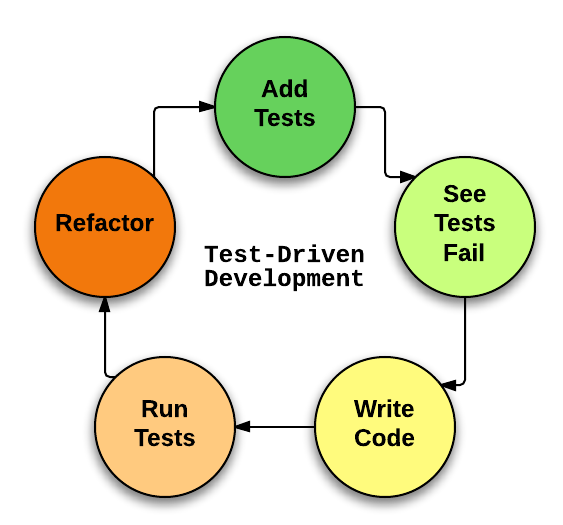
特点:先写测试用例,再写业务代码
BDD
Behavior Driven Development 行为驱动开发
领域特定语言描述用户行为,定义业务需求,让开发者集中精力于代码的写法而不是技术细节上。着重在整个开发层面所有参与者对行为和业务的理解
特点:关注行为,不关注具体实现细节
目的
- 保证代码的质量,验证功能完整性
金字塔

测试框架
| 名称 | 功能 | 特点 | 说明 | Star |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jest | 断言 仿真 快照 报告 Mock | 开箱即用 基于Jasmine发展而来 JSDOM虚拟环境 | Unit | 33.8K |
| Mocha | 需集成断言等 | 需集成其他库,如chai | ~ | 20.1K |
| Karma | 提供浏览器测试环境 | 本地浏览器环境 | ~ | 11.4K |
| Cypress | 断言 仿真 快照 报告 Mock 截图 | 整体解决方案 | All | 26.4K |
| Puppeteer | 提供Chrome测试环境 | E2E | 68.1K | |
| Jasmine | 断言 报告 | No DOM No Deps | Unit | 15K |

三大框架
Angular
Karma + Jasmine + Protractor
Karma、Protractor is maintained by Angular Team.
Karma + Jasmine :Unit test、Intergration test
Protractor: E2E test
React
Jest or Test Library for react
Vue
@vue/test-utils + Jest
可选方案:
- @vue/test-utils + Mocha
- @vue/test-utils + Cypress
Karma

Jest
以Vue2为例
安装
yarn add --dev jest vue-jest @vue/test-utils babel-jest
| 名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| jest | --- |
| vue-jest | 预处理器:处理.vue文件 |
| @vue/test-utils | vue测试工具 |
| babel-jest | ES6 |
配置
babel.config.js
module.exports = {
presets: [
'@vue/cli-plugin-babel/preset',
['env', { modules: false }]
],
env: {
test: {
presets: [['env', { targets: { node: 'current' } }]]
}
}
}
jest.config.js
module.exports = {
moduleFileExtensions: [
"js",
"json",
"vue"
],
transform: {
// `vue-jest` 处理 `*.vue` 文件
".*\\.(vue)$": "vue-jest",
// `babel-jest` 处理 js
"^.+\\.js$": "<rootDir>/node_modules/babel-jest"
},
moduleNameMapper: {
// alias
"^@/(.*)$": "<rootDir>/src/$1"
},
// 覆盖率
collectCoverage: true,
collectCoverageFrom: ["**/*.{js,vue}", "!**/node_modules/**"],
coverageReporters: ["html", "text-summary"],
coverageDirectory: '<rootDir>/coverage',
coveragePathIgnorePatterns: ['<rootDir>/node_modules/', '<rootDir>/coverage/']
}
eslint
"env": {
"jest": true,
"node": true
}
使用
基本概念
断言
判断一个函数或对象的一个方法所产生的结果是否符合你期望的那个结果
describe
describe 是 Jest 的全局函数,作为一个 Test Suite 的开始,它通常有 2 个参数:字符串和方法。字符串作为特定 Suite 的名字和标题。方法是包含实现 Suite 的代码。
注:describe会形成一个作用域
describe("This is an exmaple suite", function() {
let a = 1
it("contains spec with an expectation", function() {
expect(true).toBe(true);
expect(false).toBe(false);
expect(false).not.toBe(true);
});
test("contains spec with an expectation2", function() {
expect(true).toBe(true);
expect(false).toBe(false);
expect(false).not.toBe(true);
});
});
expect
在编写测试时,通常需要检查值是否满足某些条件。expect允许您访问许多“匹配器”,这些匹配器允许您验证不同的东西。


setup and teardown
为了使某个测试用例干净的重复 setup 和 teardown 代码, Jasmine 提供了全局的 beforeEach 和 afterEach 方法。正像其名字一样,beforeEach 方法在 describe 中的每个 Spec 执行之前运行,afterEach 在每个 Spec 调用后运行。
describe("An example of setup and teardown)", function() {
var gVar;
beforeEach(function() {
gVar = 3.6;
gVar += 1;
});
afterEach(function() {
gVar = 0;
});
it("after setup, gVar has new value.", function() {
expect(gVar).toEqual(4.6);
});
it("A spec contains 2 expectations.", function() {
gVar = 0;
expect(gVar).toEqual(0);
expect(true).toEqual(true);
});
});
mock
测试场景
异步
Promise
test('the data is peanut butter', () => {
return fetchData().then(data => {
expect(data).toBe('peanut butter');
});
});
Async/Await
test('the data is peanut butter', async () => {
const data = await fetchData();
expect(data).toBe('peanut butter');
});
setTimeout
组件
import { mount } from '@vue/test-utils'
import HelloWorld from '../src/components/HelloWorld.vue'
describe('HelloWorld', () => {
test('has class name', () => {
const wrapper = mount(HelloWorld)
expect(wrapper.classes()).toContain('hello')
})
test('trigger a click', async () => {
const wrapper = mount(HelloWorld)
const message = wrapper.find('#message')
await wrapper.find('button').trigger('click')
expect(message.text()).toBe('testFunction has been clicked!')
})
})